Our worldwide distributors can help you find the best solution for your needs

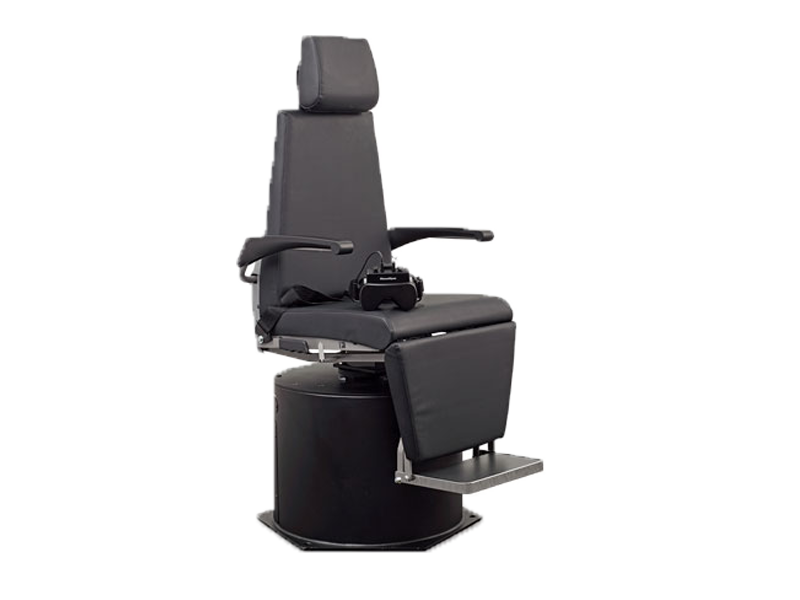
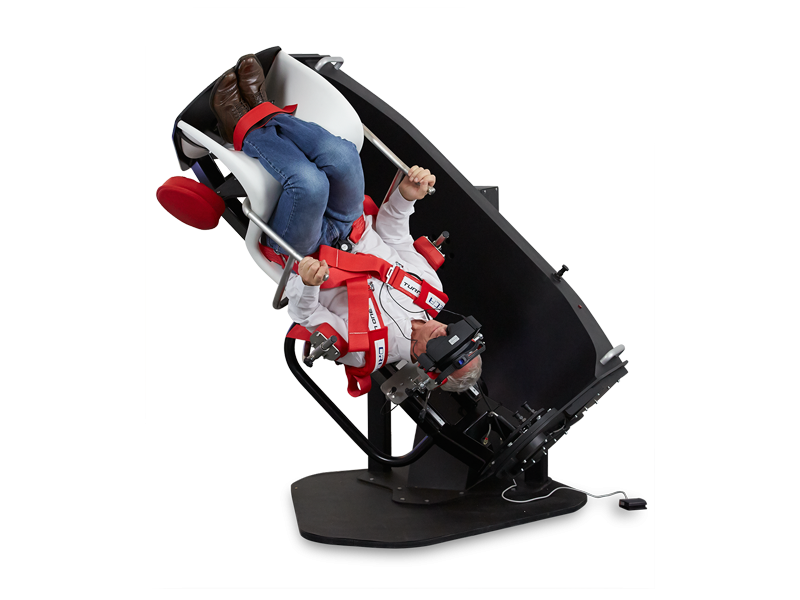
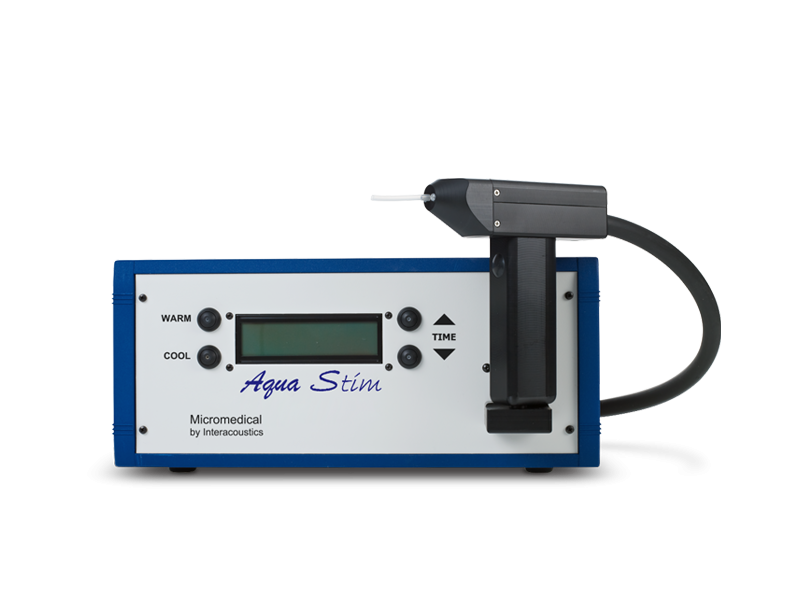
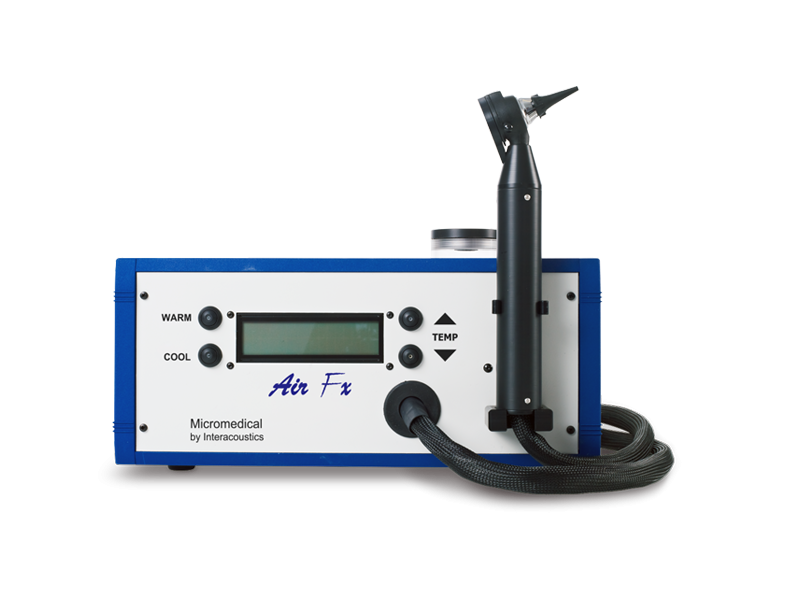
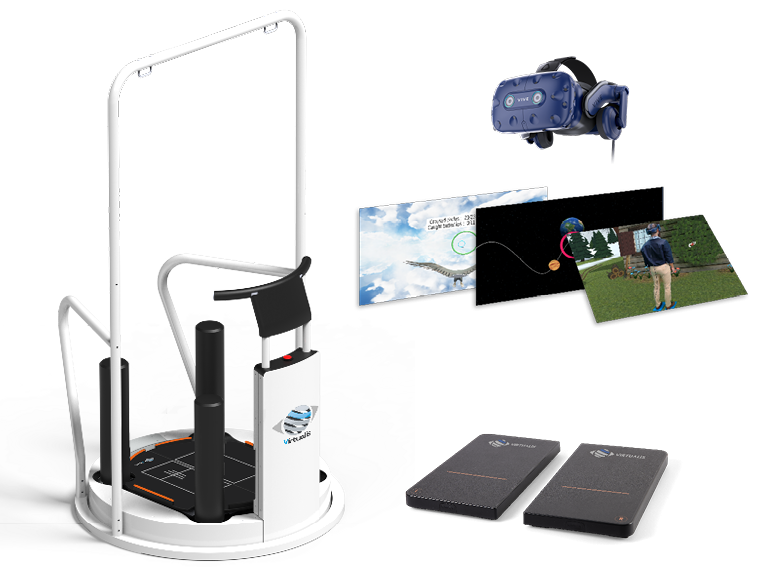
Balance testing equipment
Frequently asked questions
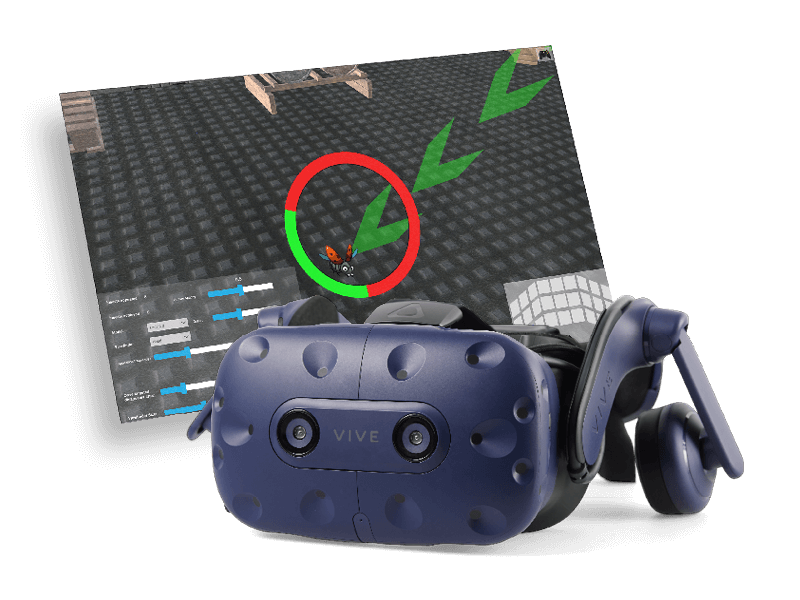
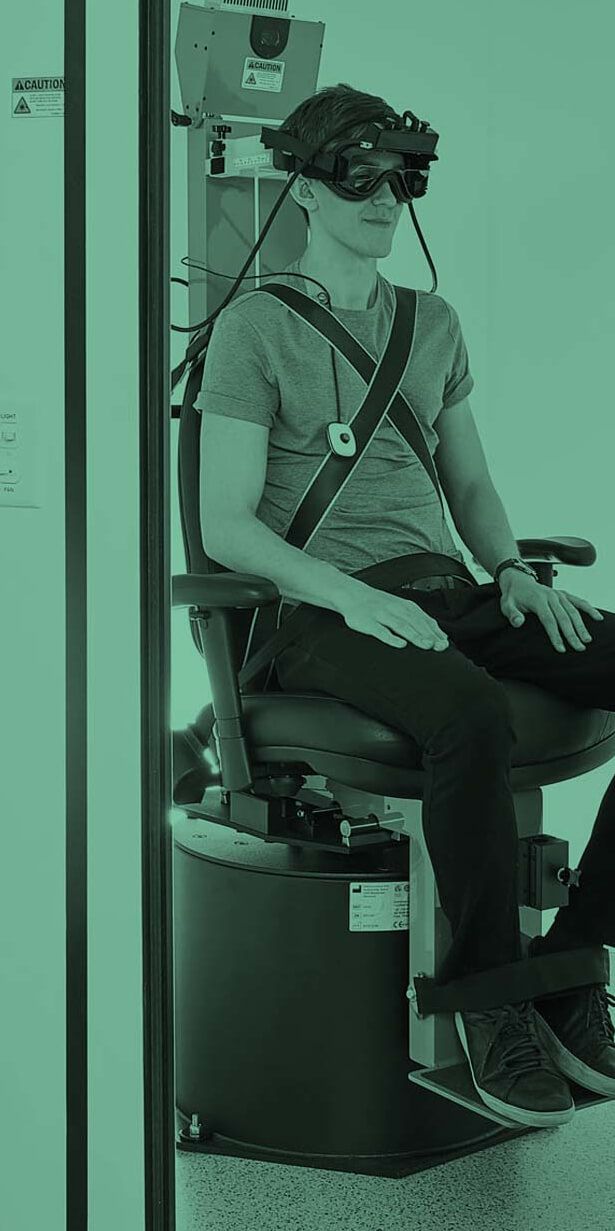
Videonystagmography (VNG) is a vestibular assessment of peripheral vestibular systems located in the inner ear and of the central motor functions of eye movement. VNG testing uses goggles with infrared cameras to track eye movements with fixation removed during visual stimulation and positional tests.
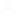
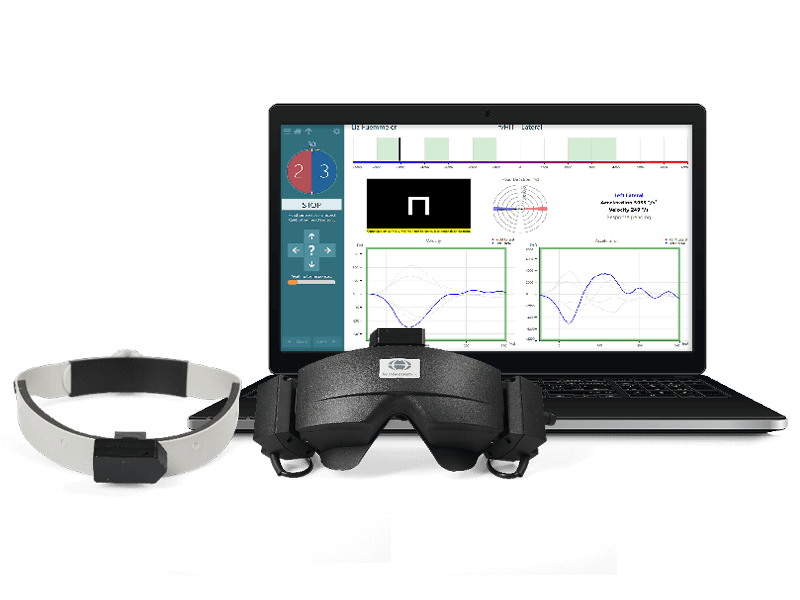
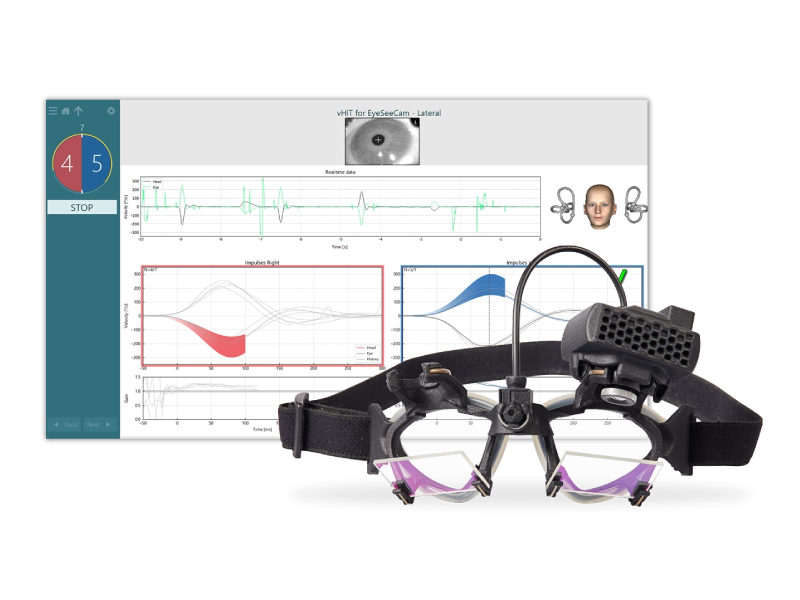
The video head impulse test (vHIT) is a high-frequency test of the vestibulo-ocular reflex (VOR). It tests the function of all six semicircular canals in the peripheral vestibular system and offers a supplementary assessment to rotary chair testing and caloric irrigation. Compared to the traditional clinical head impulse test (cHIT) that is conducted with direct observation of the eye, the vHIT can objectively detect and record overt and covert refixation saccades. You can document and use these measurements to identify any impairment or abnormality in the generated VOR.
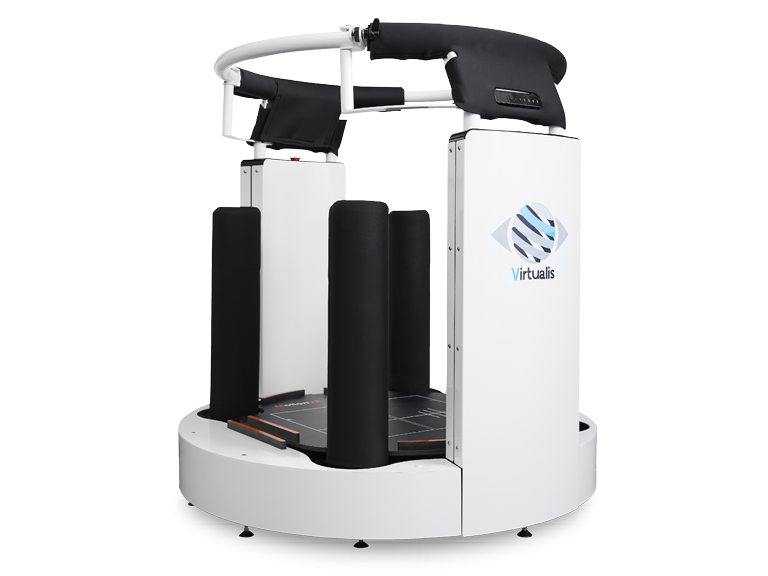
Computerized dynamic posturography (CDP) is a scientific framework for understanding the control of balance and postural stability. It utilizes a force plate to measure the center of pressure in the anterior posterior and lateral directions. CDP can objectively quantify functional impairments and is ideal for physical therapy and rehabilitation exercises.
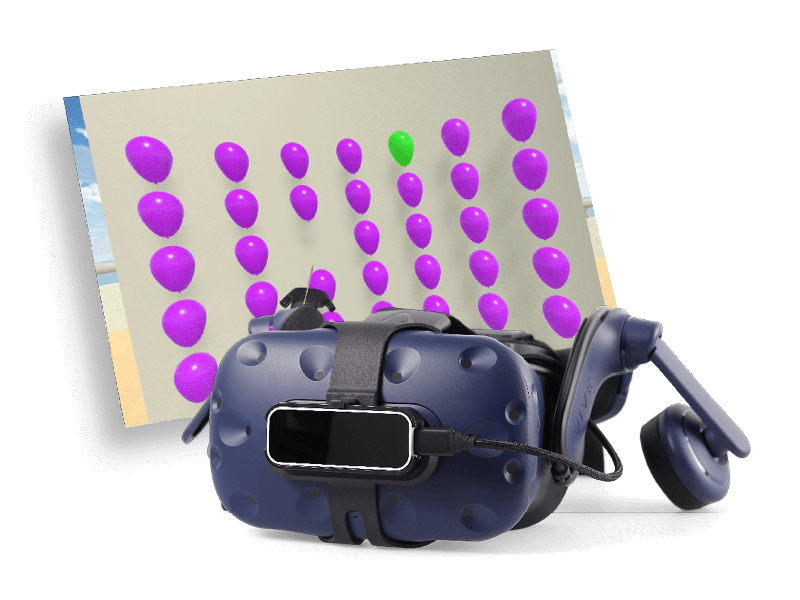
The dynamic visual acuity (DVA) test is a functional assessment of visual acuity during head movements. The goal of DVA testing is to identify the smallest target a patient can see with their head moving at a fixed velocity of 100 degrees per second. With the data that the computerized method offers, one can quantify the loss of acuity during active head movement and differentiate between directional loss of acuity.