Our worldwide distributors can help you find the best solution for your needs

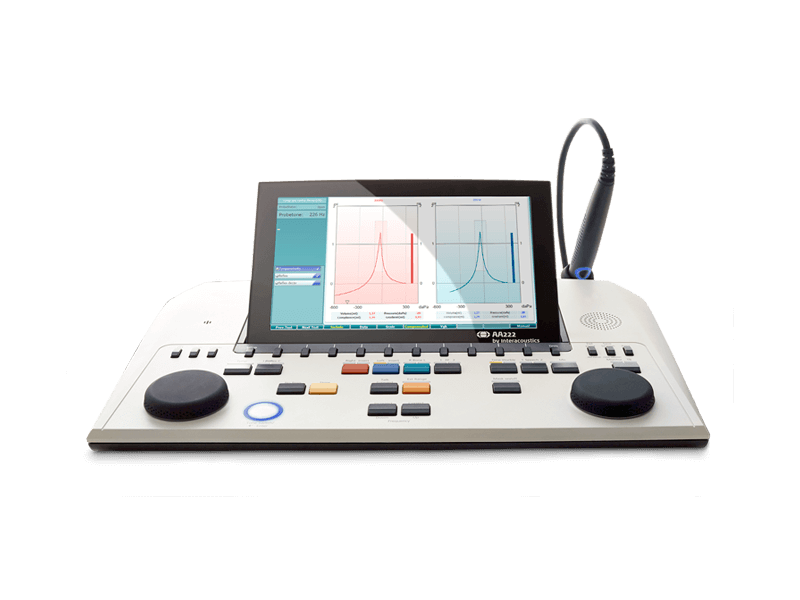
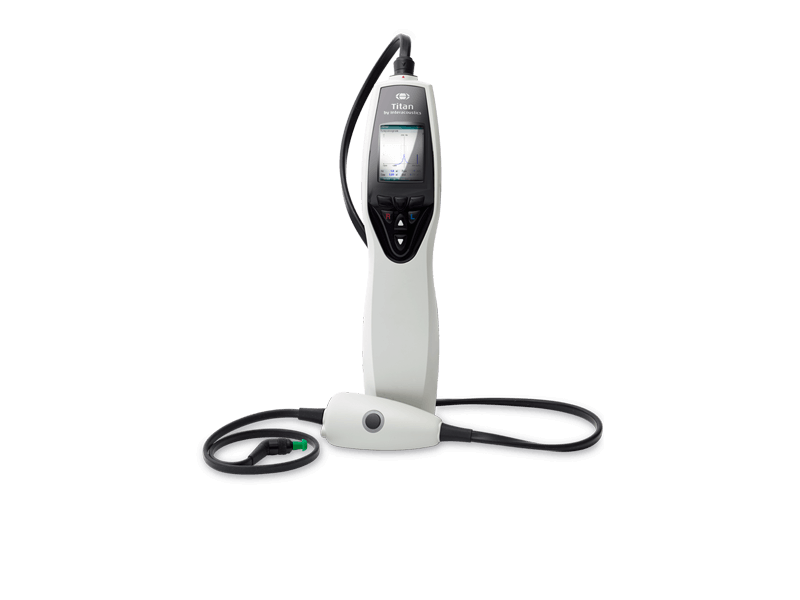
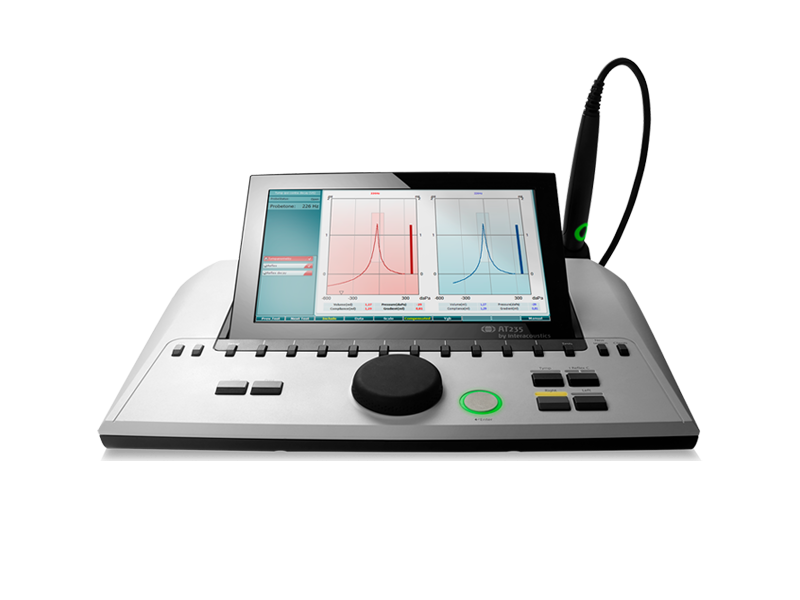
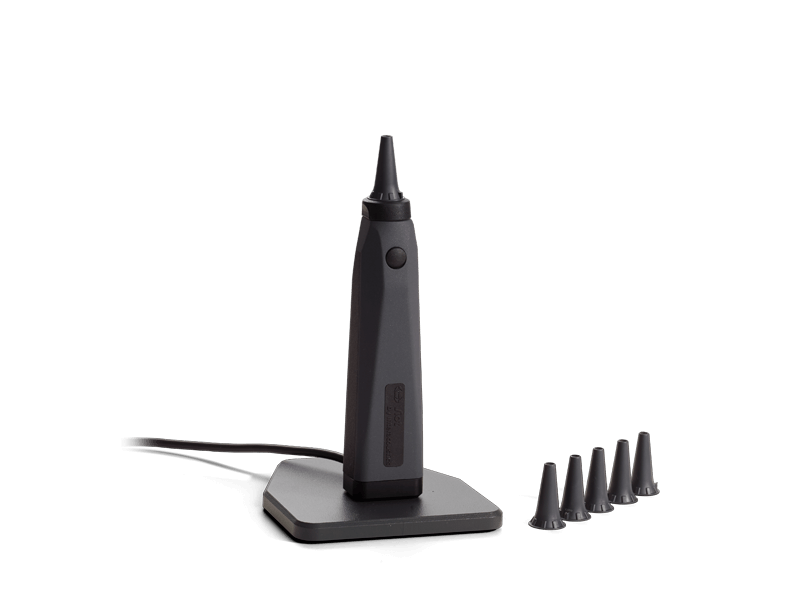
Tympanometers
Frequently asked questions
What is a tympanometer?
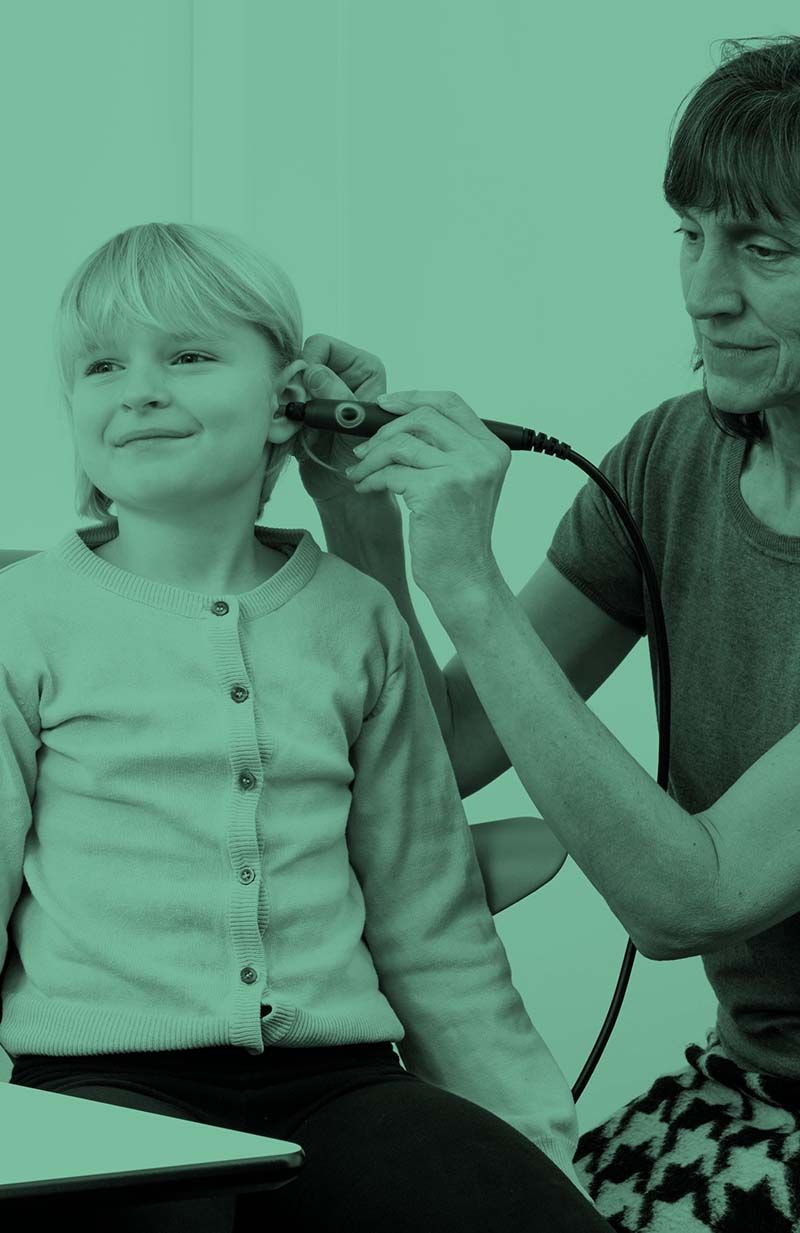
A tympanometer is an instrument used to measure middle ear function. There are several different types; some can only do a few tests such as tympanometry and acoustic reflex measurements. More advanced tympanometers can provide a more thorough assessment of the middle ear. This includes the ability to identify middle ear diseases.
What is tympanometry?
Tympanometry is a test where both negative and positive pressure is applied to the middle ear alongside a constant probe tone. Tympanometry assesses how much of the probe tone is absorbed into the middle and inner ear, and how much is reflected. This allows clinicians to form a picture of how the tympanic membrane acts and functions.
What is a tympanogram?
A tympanogram is a graph produced by tympanometry. It shows the movement of the tympanic membrane and is most often cone-shaped. The peak of a tympanogram is where the eardrum is balanced between negative and positive pressure. By using a template such as Jerger’s classification, it is possible to determine if the tympanic membrane moves freely or if a disorder is present.
How to read a tympanogram?
To read a tympanogram, it is important to look at its shape and the values for ear canal volume, pressure, gradient, and compliance (also known as admittance). The amount of ear canal volume (ml/mmho) depends on how deep the probe tip is inserted. Pressure (daPa) is the peak pressure, thus the peak of the tympanogram. Gradient (daPa) is the steepness of the tympanogram. Compliance (ml/mmho) shows how much energy is being absorbed by the ear and how much is reflected to the probe tip.
Most popular product training.
Contact your local distributor
Our world-wide experts and distributors can help you find the best solution for you and your clinic. They also know what products are available in your market. Fill out the form and your local distributor will contact you with more information.
Distributors
Purchase from one of our trusted distributors.
Support
Need product training? Visit our training site to find answers.